Adding 3D Visualization to the SPARQL Query Loop
August 30th, 2018
Erwin Folmer
(e.j.a.folmer@utwente.nl),
Wouter Beek
(Wouter.Beek@kadaster.nl)

Before we start…
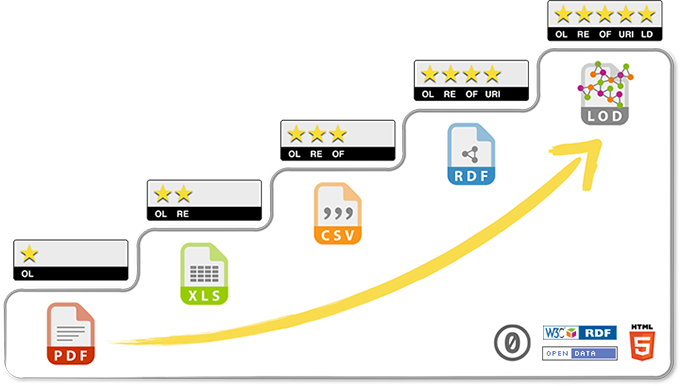
What is Linked Data?
Public Data on the Map (https://pdok.nl)
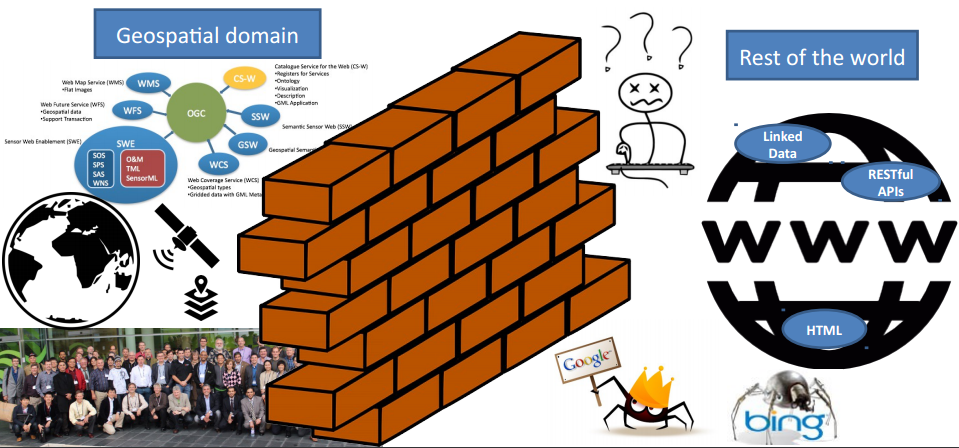
Spatial Data & the Web
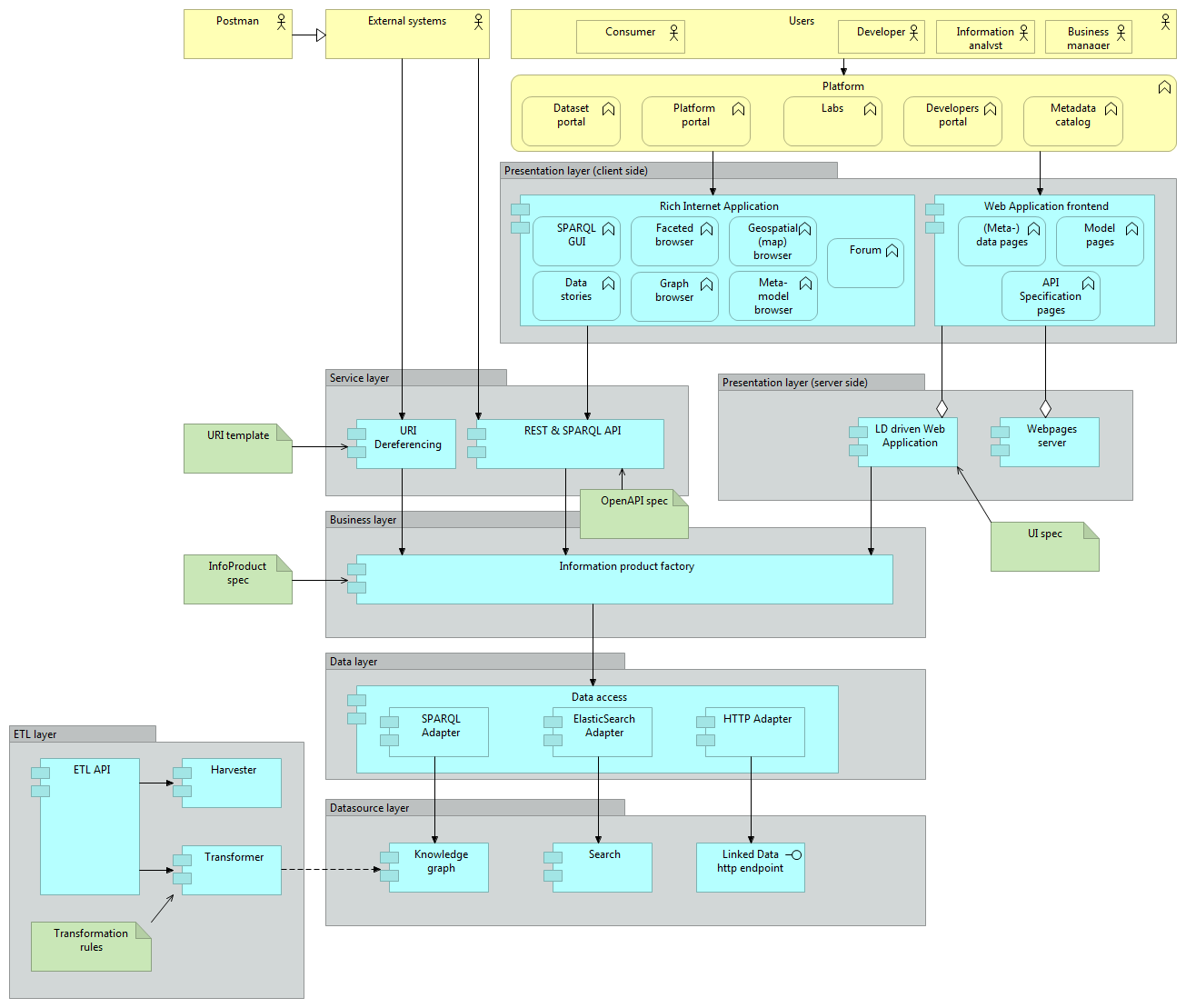
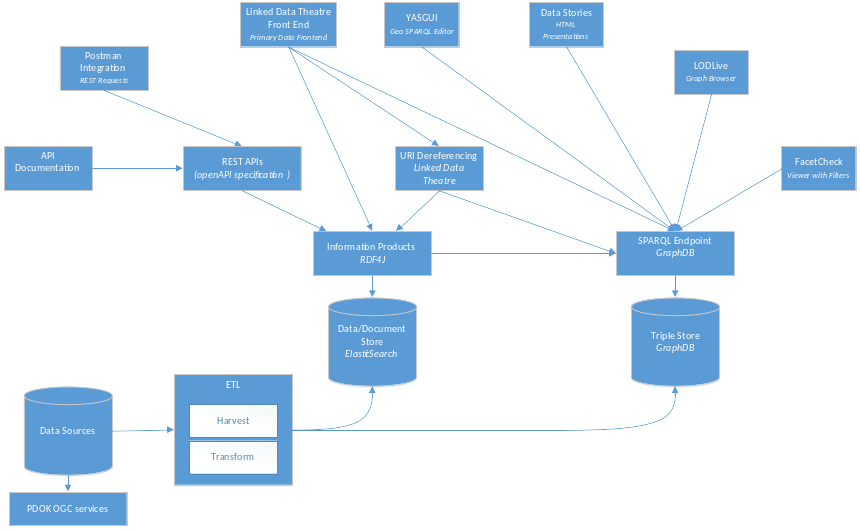
YASGUI: Yet Another SPARQL GUI
Previously extended with 2D GIS functionality (FOSS4G 2017).
A practical approach for accessing GIS datasets with SPARQL.
But then we did some buzzword matching for management…
3D Linked Data Visualisation
(It does not only sound cool, but it also makes sense…)
Benefits of 3D
- Interpretability
- We are used to interpreting and interacting with a 3D world.
- Expressiveness
- The z-axis gives an additional dimension to plot (statistical) data on.
- Multiple perspectives
- Allows for different views for the same objects (e.g., building).
Cadastre use cases for 3D SPARQL
- Displaying one building with multiple businesses and apartments in it.
- Drone no-fly zones contain height information.
- Emergency services must determine the reachability of an appartment within a building.
REPL: read-eval-print-loop
A well-known concept from programming, applied to query writing:
- Read
- Process a user-entered query.
- Evaluate
- Calculate the result set for the user query.
- Show the result set to the user.
- Loop
- The user inspects the results and changes the query.
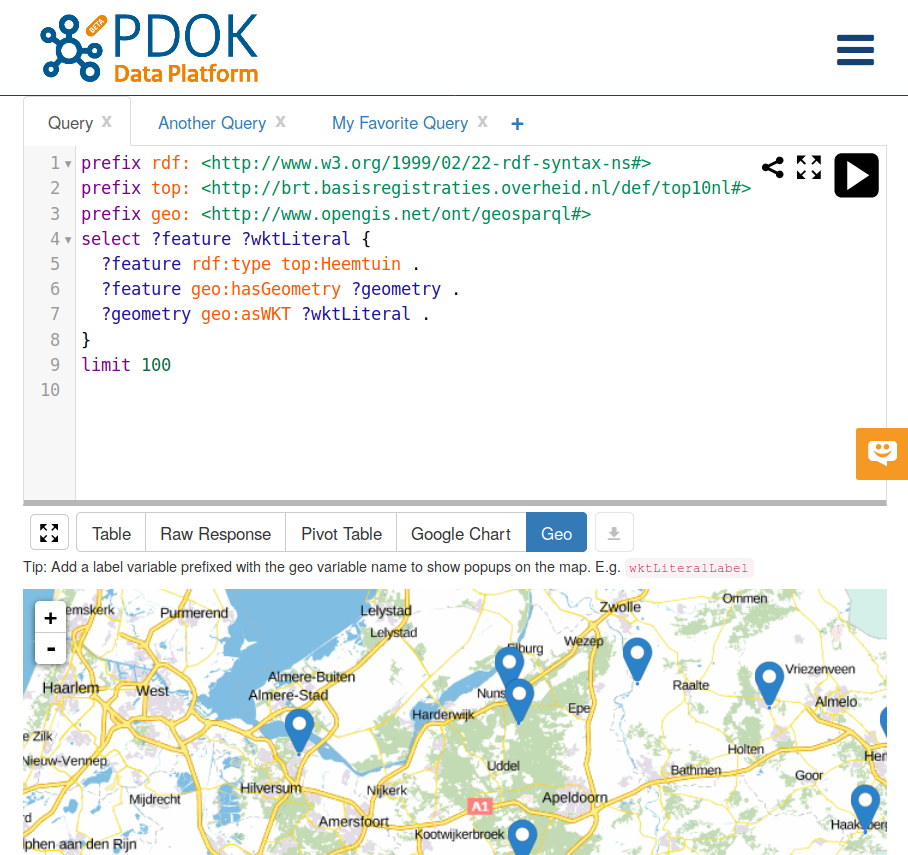
REPL: Read (1/2)
REPL: Read (2/2)
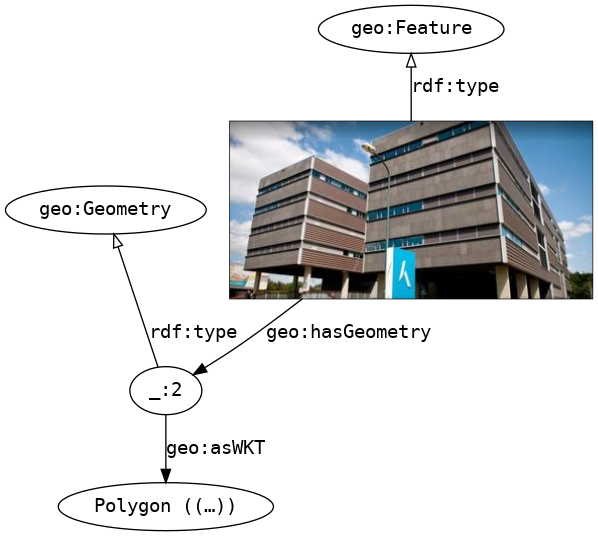
REPL: Evaluate
3D support in triple stores:
- Most stores do not implement 3D GeoSPARQL syntax, but some do.
- Most stores have bad performance for 3D geo-spatial queries, but some have good performance.
- Some stores change the 3D data merely by loading it, e.g., turning it into 2D data.
- Some stores cannot load larger 3D shapes.
- Commercial triple stores are not necessarily better than FOSS (if fact: they are often worse).
REPL: Print
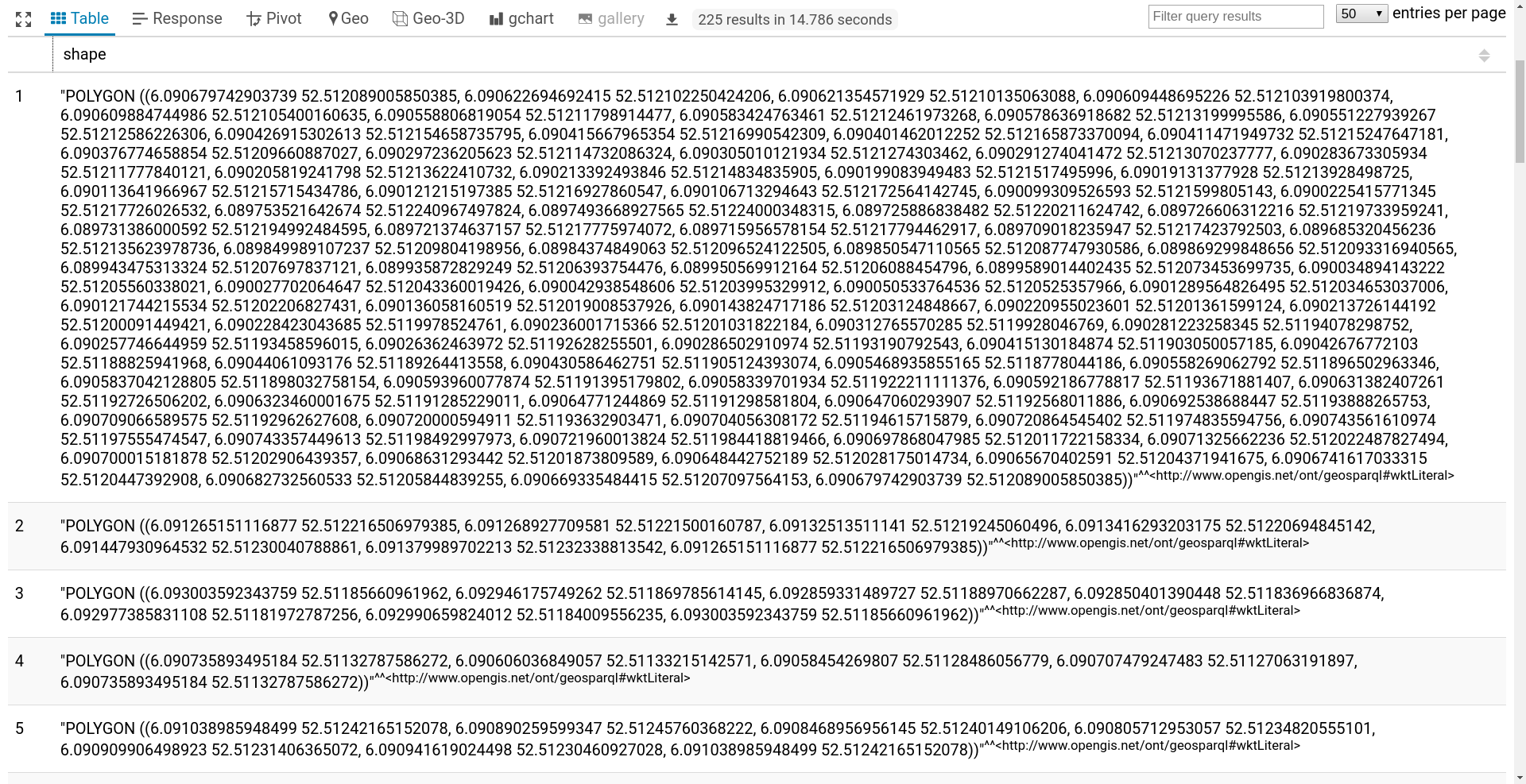
REPL: Print
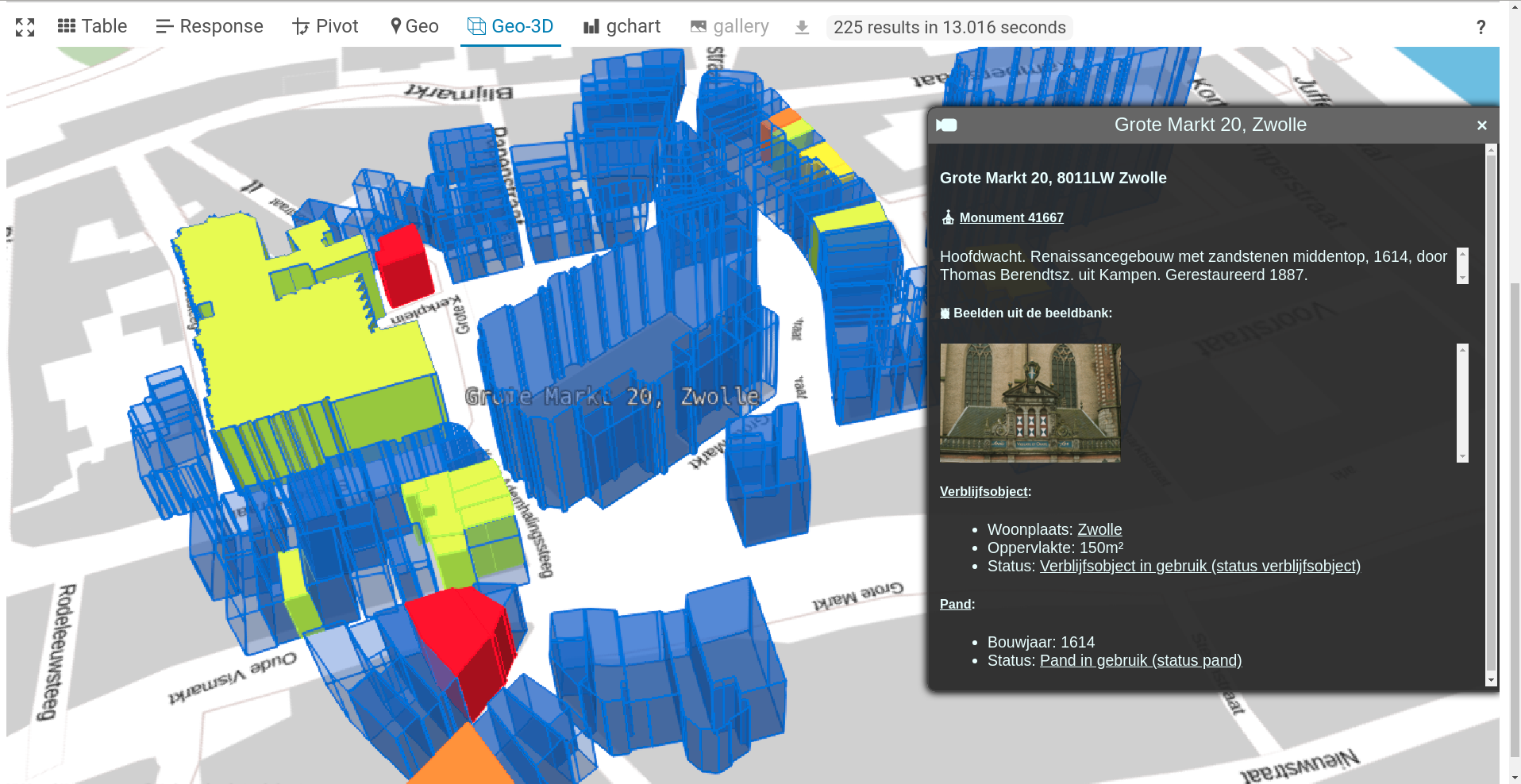
Examples of 3D SPARQL Queries
Geo-3D query
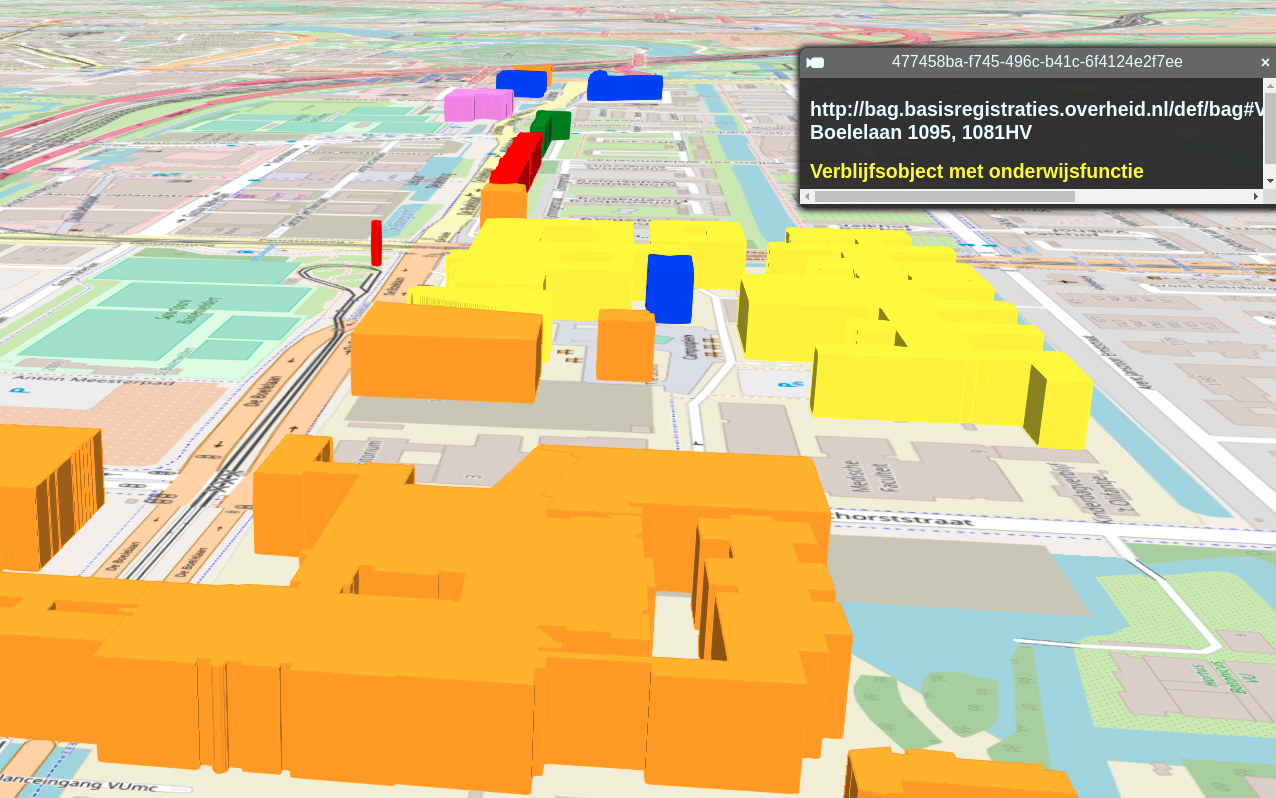
- Living space
- Shopping
- Offices
- Education
- Health
- Sport
Querying 4 datasets

- Cadastre
- Building Registry (BAG) 🏠
- Chamber of Commerce (KvK)
- Companies 🏢
- Cultural Heritage Agency (RCE)
- Monument registry & imagebank ⛪
- Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO)
- Energy labels 🗲
Energy labels 🗲
Queries the following datasets:
- BAG (KDP Productie)
- RVO energielabels (KDP Labs)
Monuments ⛪
Queries the following datasets:
- BAG (KDP Productie)
- RCE beeldbank (KDP Labs)
- RCE monumenten (KB endpoint)
Chamber of Commerce 🏪
Queries the following datasets:
- BAG (KDP Productie)
- Kamer van Koophandel bedrijven (KDP Labs)
Number of businesses 🏬
Queries the following datasets:
- BAG (KDP Productie)
- CBS buurten (KDP Labs; binnenkort KDP Productie)
Experimental: 3D rooftops
Experimental: Apartments within a building
3D variable bindings
Implemented by binding variables that follow specific naming patterns, compatible with SPARQL 1.1.
| Concept | Variable name |
|---|---|
| Shape | ?var |
| Colour | ?varColor |
| Complex label | ?varLabel |
| Extrusion | ?varHeight |
| Offset | ?varZ |
| Simple label | ?varName |
Future challenges
- Display textures on 3D shapes
- Store and retrieved detailed 3D models (BIM)
- More 3D data as Linked Data, e.g., rooftops, underground structures
- Integration into YASGUI production version
YASGUI: Yet Another SPARQL GUI

Previously extended with 2D GIS functionality (FOSS4G 2017).
Now extended with 3D GIS functionality (FOSS4G 2018)
So what's next for FOSS4G 2019? 😉
Thank you for your attention!
Erwin Folmer
(e.j.a.folmer@utwente.nl),
Wouter Beek
(Wouter.Beek@kadaster.nl)
